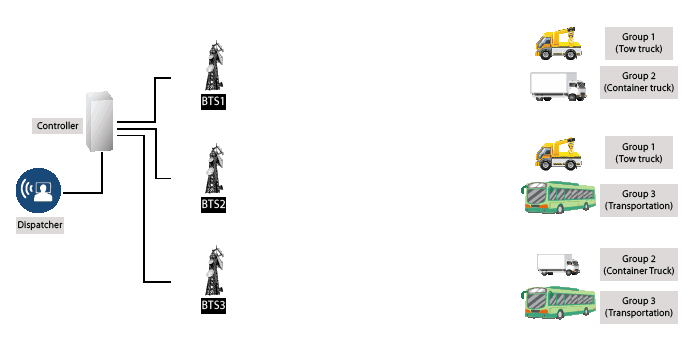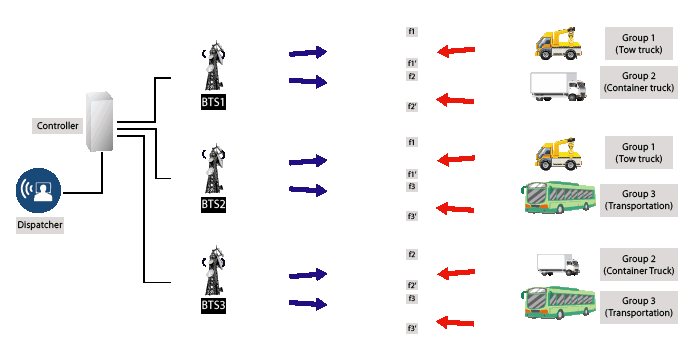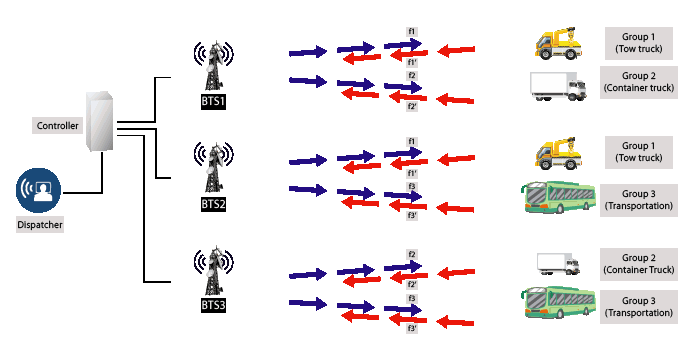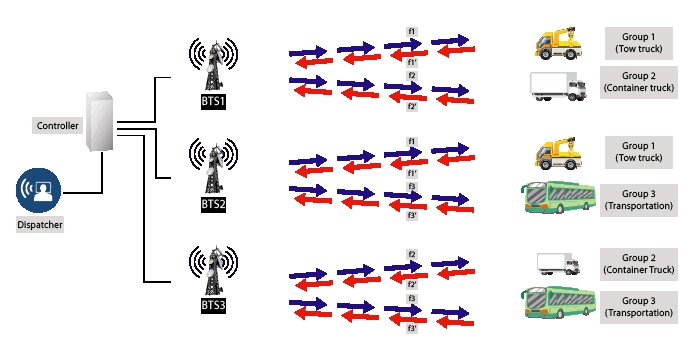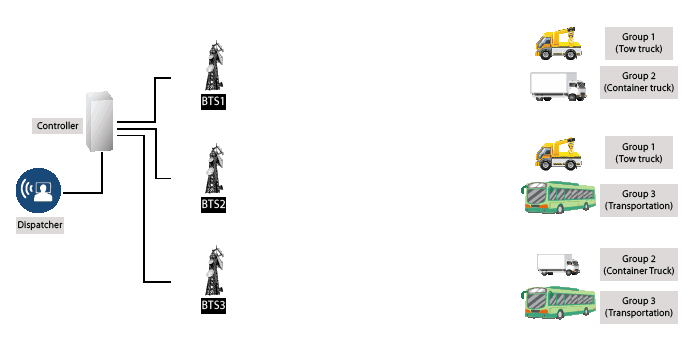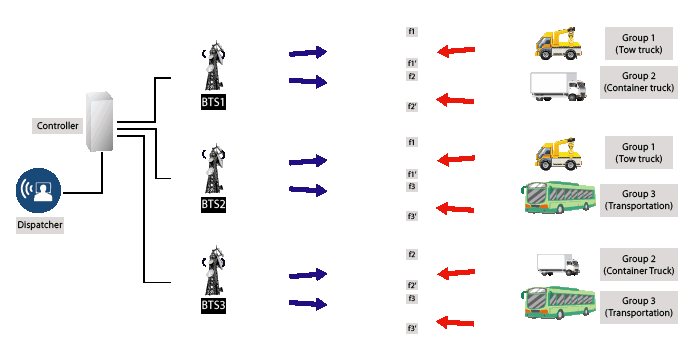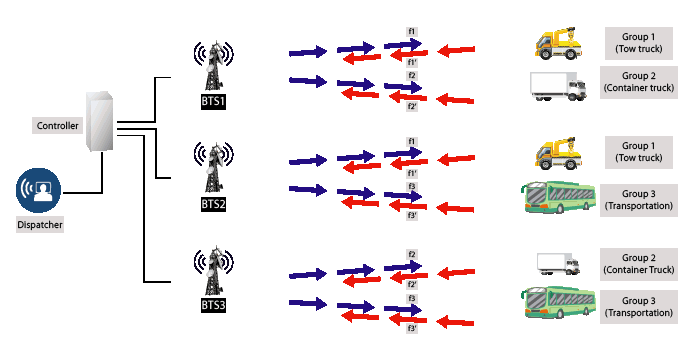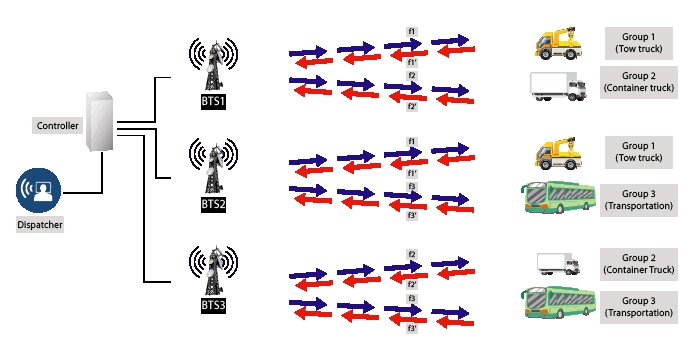Trunked Radio
- Home
- Trunked Radio
- Introduction
Introduction
- A two-way mobile radio system that consists of multiple–channel base repeater stations and their control stations, serving a number of mobile terminal.
- Offers a list of applications such as transmission of voice, data, image, paging, facsimile, short messaging and Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) interconnection.
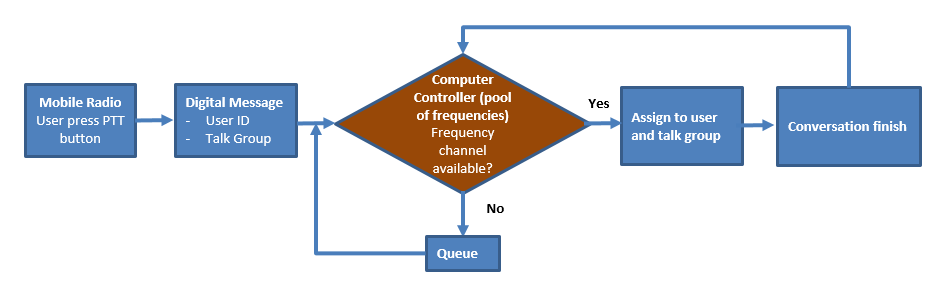
- A computer controlled radio system (technically more complex than conventional radio)
- Assignment of frequency by computer control and frequency is not fixed to specific group or user.
- Commonly to accommodate high number of users.
- How its work: When the user press the push-to-talk radio button, the computer will automatically assign the user and user’s talk group on the available frequency channel
Technologies
- Terrestrial Trunk Radio (TETRA)
Based on a 4 slots of Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) with 25 kHz physical radio channel bandwidth. TETRA standard supports trunking mode and IP-based TETRA solutions are available.
- Association of Public-safety Communications Officials Project 25 (APCO-P25)
A common standard for DTRS used by public safety agencies in North America to enable them to communicate with other agencies and mutual aid response teams in emergencies.
- Next Generation Digital Narrowband (NXDN)
A digital air interface protocol for mobile communication.
- Digital Mobile Radio (DMR)
A standard developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) under its Electromagnetic compatibility and Radio spectrum Matters (ERM).